Twitter offers a public platform to share ideas and connect. But like most social networks, it collects user data for targeted advertising. One concern is location tracking on Twitter even when you aren’t using the app.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll look at how Twitter gathers location data, the risks of location tracking, and steps you can take to limit sharing your location on Twitter.
Table of Contents
Understanding Twitter Location Tracking
First, let’s examine how and why Twitter incorporates location signals into your profile and experience:
Types of Location Data Twitter Collects
There are a few ways Twitter can identify your location:
- GPS Coordinates: Your precise lat/long when tweeting via mobile. Considered precise location data.
- WiFi Networks: Nearby WiFi routers and SSIDs that indicate a general area like a coffee shop.
- Mobile Carriers: The towers/network you connect to via cellular data pinpoints region.
- IP Addresses: Your device’s IP maps to a city-level location in most cases.
- Linked Profiles: Other social networks like Instagram with location listed.
- User Input: Bio location, tagged tweets, posts mentioning travel.
From this mix of signals, Twitter can identify your time zone, city, and specific coordinates when active on mobile.
Why Twitter Uses Location Data
Location helps Twitter understand users for:
- Localization: Providing location-relevant content like nearby events or trends.
- Advertising: Targeting ads based on your city and points of interest.
- Legal Compliance: Certain countries limit content by geography.
- Safety: Identifying bad actors and avoiding restrictions via VPNs.
- Analytics: Understanding user demographics and behaviors.
Like most platforms, Twitter uses location data to improve the user experience, target opportunities to monetize via advertising and reduce misuse risk.
Twitter’s Location Tracking Policy
Under its privacy policy guidelines, Twitter takes a transparent approach to location data:
- Provides examples of specific location signals they use.
- Explain the types of location data they collect and why.
- Offers controls to limit location sharing and tracking.
- Confirms they may still derive approximate location even if settings disable tracking.
- States they do not sell raw location data, only use it internally.
Overall, Twitter’s location policy is communicated and provides options for user control. However, location can never be fully disabled due to the nature of mobile connectivity.
Risks and Concerns Around Twitter Location Tracking
While location offers helpful features, constant tracking also carries potential downsides users should evaluate:
1. Privacy Invasion
Precise location hints at activities, habits, identities, and relationships some may consider private. Like who you visit or attend events with.
Even approximate city-level tracking provides personal context to many who want to control access.
2. Security Vulnerabilities
Surreptitious location tracking by hackers or spyware is a rising threat vector. Stalkers or bad actors can monitor your movements digitally.
Location analytics profiles also create attractive data sets cyber criminals desire to understand people’s patterns and exploit.
3. Data Commercialization
While Twitter states they don’t sell location data directly, they enable location-based advertising.
This allows advertisers to target consumers based on where they are. Users need more visibility into how location gets used for ads.
4. Unfair Pricing or Access Based on Location
Dynamic pricing or exclusive offers based on location raise concerns over equitable access to products and services.
Poor enforcement of bans on using location for discrimination also persists in areas like housing and employment.
5. State Surveillance Potential
Location insights appeal to governments looking to track dissidents, critics, and minorities. Expanding surveillance powers leverages digital data.
Authoritarian regimes can force platforms to hand over user location data that may put certain groups at risk.
6. No Truly Opting Out
Even with location services disabled, mobile networks and WiFi still provide approximate locations. TRULY turning off tracking requires avoiding modern connectivity.
For digital natives, that represents an unfair trade-off between privacy and social participation.
As with all data collection, the risks require evaluating trade-offs. However, location tracking stands out, given the intimacy of knowing a person’s movements and geography. Most users want finer controls over who can access their location insights.
Twitter Location Settings: Available Controls
In response to privacy concerns, Twitter provides options to manage location tracking:
Turn Off Location Services Entirely
You can disable location services for the Twitter app within phone settings. This prevents Twitter from accessing your precise GPS latitude/longitude when tweeting.
However, it limits location-based features on Twitter, like local trends and events. Your experience will be less tailored.
And Twitter can still infer approximate location from mobile networks and IP signals. So disabling location services only limits precision but doesn’t fully anonymize location.
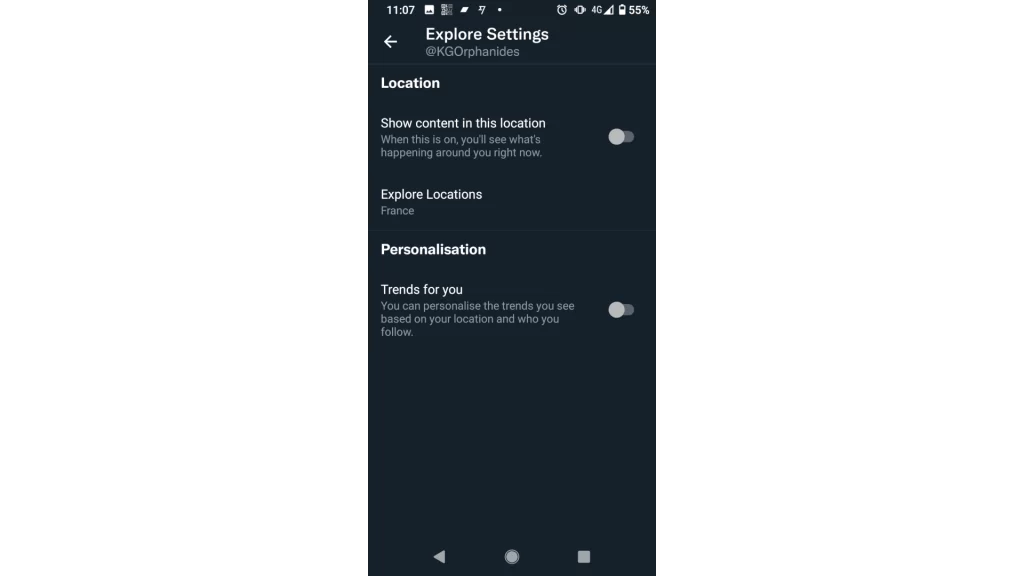
Enable Location Precautions on Twitter
Within Twitter’s app, you can also toggle on additional location precautions:
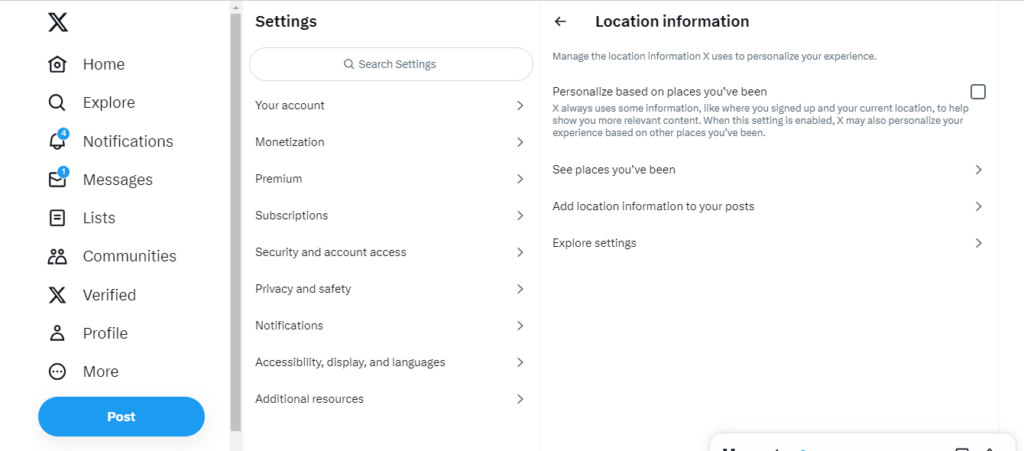
- In-app Settings, go to Privacy and Safety > Location Information
- Toggle “Precise Location” off
This adds protection beyond just disabling GPS access. Twitter cannot use Wi-Fi networks or other identifiers to pinpoint your location.
However, Twitter will still identify an approximate location to comply with laws and show you relevant content. This setting tells Twitter only to track city-level data rather than specific coordinates.
Review Twitter’s Location Dashboard
Twitter provides a map-based location dashboard so you can see where it has identified you being located:
- Go to Settings > Privacy and Safety > Location Information
- Select “View Location Dashboard”
This shows a circle map indicating the latitude/longitude Twitter has tracked, accompanied by date/time.
Review this dashboard periodically to check if Twitter’s location tracking aligns with your movement and online activity. Make sure no errant or suspicious locations appear.
Disable the Use of Linked Accounts
Twitter can also deduce location from other social profiles you link to your Twitter account that show location data publicly.
To prevent Twitter from gathering location from your linked profiles:
- Go to Settings > Privacy and Safety > Use Linked Accounts
- Toggle Linked Accounts to Off
This ensures Twitter only relies on its first-party relationship with your account rather than importing location data from your broader social media footprint.
Evaluate Third-Party App Permissions
Many apps request location access for additional features like filters or stickers. But this also enables wider location tracking.
Audit which third-party apps have location authorization through your Twitter account and revoke access if not needed:
- Go to Settings > Security and Account Access > Apps and Sessions
- Review all authorized apps and remove those no longer used
Reconsider which apps truly require location access rather than allowing it by default. Restricting third-party app permissions limits location exposure.
Going Beyond Twitter’s Settings to Disable Tracking
If Twitter’s on-platform controls still feel inadequate, additional options outside the app exist to curtail location tracking:
Use a VPN or Proxy Service
Routing your traffic through an intermediary server via a VPN or proxy hides your real IP address and wifi data Twitter would otherwise collect. It allows spoofing or scrambling location signals.
Free browser extensions like Hide My Location provide quick VPN access to mask your location on Twitter.
However, VPNs reduce internet performance. And Twitter can still deduce general region from the intermediary IP, with lower accuracy.
Try a Firewall or Ad Blocker
Firewalls and ad/tracker blocker browser extensions filter out background requests to location data aggregators. This shuts down a data pipeline Twitter relies on.
For example, extensions like Privacy Badger block Twitter’s requests to Foursquare, which informs location tracking. Cutting off this backend supply of intel makes Twitter’s job harder.
But, extensive blocking can break site functionality. And determined platforms have other sneaky ways around blockers, like fingerprinting. It’s a constant cat-and-mouse game.
Leverage Browser/App Settings
Browsers like Chrome allow managing site permissions to access location, camera, microphone, and notifications.
Denying Twitter location access in browser settings reinforces restrictions beyond just within the app.
Apple iOS and Android also include toggles to disable location per app for additional control. Every privacy boundary you can enable helps.
Alter Your Twitter Activity Patterns
Location tracking relies heavily on routine patterns and history. Varying your interactions challenges assumptions.
Using Twitter in new places, traveling, and tweeting from different devices makes tracking your movements tougher. Don’t be too predictable!
Avoid Location-Revealing Content
Be mindful of tweets, images, check-ins, and hashtags that reveal your location. Don’t freely advertise your geography.
Stay vague about physical whereabouts where possible and mix up any specifics occasionally.
Practice General Social Media Privacy Hygiene
Thwarting location tracking should be part of broader habits like:
- Enabling MFA everywhere
- Securing logins/devices
- Being wary of third-party app permissions
- Limiting ad targeting settings
- Periodically reviewing the visibility of profile info
- Not tying your identity to handles
Comprehensive privacy requires combining location protections with otherwise social platform practices!
Twitter Location Tracking Compared to Other Social Networks
To put Twitter’s location tracking practices into context, how does it compare with other top social platforms users should be aware of:
| Platform | Location Tracking Policy | Controls Offered |
|---|---|---|
| Transparent about what is collected; states data not sold | Can disable precise location; general area still inferred | |
| Less transparency; likely tracks via Meta Pixel | Limited controls; requires not sharing or tagging location | |
| Extensive data collection via Pixel; uses location to aid targeting | Can review locations tracked and turn off location history | |
| Snapchat | Leverages bitmoji locations and geofilters; shares data through Pixel | Geofilters require location access; settings disable sharing |
| TikTok | Many inconsistencies in reported collection practices | Can disable access and hide city, but claims still track region |
| YouTube | Location inferred via watch history and IP addresses | Can pause watch and search history to limit tracking signals |
Twitter is reasonably transparent compared to platforms like Instagram and TikTok, with murkier practices. But no social network allows turning off location completely as long as you use mobile apps. Expect trade-offs managing the privacy risks versus utility location provides.
Location Tracking Guidelines from Privacy Advocates

Beyond Twitter’s specific controls, privacy groups like the EFF and PEN America recommend general good practices around location data:
- Avoid syncing contacts/social accounts that may reveal location without your knowledge or consent
- Selectively review location timeline data logged by platforms to identify any discrepancies
- Limit location access to apps that don’t require it for core functionality
- Evaluate whether location-based features are worth the privacy trade-off for your personal threat model
- Lobby governments to mandate location data protections and consent requirements
- Support consumer protection laws that prohibit discrimination based on location-derived demographics
- Encourage companies to enhance transparency on how they handle and derive value from location data
Be more critical of location tracking than accepting it as the norm. Scrutinize the benefits against risks. And speak up to demand companies and legislators limit the exploitation of location insights.
The Future of Location Tracking on Social Media
As users become more aware of privacy impacts, how could location tracking evolve on Twitter and other top social platforms going forward? Several possibilities stand out:
- Stronger Regulations: Stricter laws on collecting and monetizing location data without clear opt-in consent from users. Similar to GDPR protections in Europe.
- Geofencing Restrictions: Preventing location tracking and ad targeting around sensitive locations like health centers and places of worship where privacy expectations are high.
- Local Device Processing: Keeping location insights only on-device rather than uploading to company servers where exploitation potential is higher.
- Blurring and Noise: Adding fuzziness and uncertainty into location signals to prevent pinpoint tracking.
- Decentralized Data Management: Giving users control via local storage and encryption rather than relying on corporate platforms.
- Blockchain-Verified Consent: Enabling users to pre-approve location collection via blockchain tokens to strengthen opt-in control.
- Location Data Unions: Pooling user location data in privacy-preserving data trusts/cooperatives so value stays with consumers rather than companies.
- Spatial Computing: On-device processing of location to power augmented reality features without raw tracking.
Evolving technology, decentralized systems, policy, and ethical data handling all play a role in balancing innovation and privacy. Users are increasingly wary of unchecked location tracking. Expect location privacy to remain a catalyst for rethinking data rights. Twitter and its peers must adapt location practices to Web3 and spatial computing expectations.
Key Takeaways About Managing Location Tracking on Twitter
A few core points to remember about location tracking controls on Twitter:
- Twitter gathers location signals from mobile, Wi-Fi, IP, and profiles to customize the user experience and target advertising.
- Risks include privacy invasion, stalking potential, and supporting discrimination or state surveillance.
- Twitter is transparent about collection compared to some platforms but still lacks total opt-out.
- You can disable precise location tagging and sharing and limit linked accounts and permissions.
- Additional options like VPNs and ad blockers exist but require trade-offs. Every solution is still being perfect.
- Future possibilities span regulations, geo-fencing, device processing, and decentralization to balance innovation and privacy.
- Users should regularly audit location settings as threats evolve and evaluate whether tracking-based features are worth the privacy compromise.
The Bottom Line
Location tracking on social media platforms remains fraught with many tensions between benefits and risks. But the overall trend points toward empowering user control, consent, and transparency from companies like Twitter.
Perfect solutions are still being determined, given the nature of mobile connectivity, tying location to identity. However, persisting in limiting tracking, scrutinizing practices, and exploring decentralization can balance innovation with privacy.
Through sound data hygiene and advocacy, users concerned about location tracking have paths to exercise agency over privacy. While Twitter and peers adapt at a measured pace, individuals can take steps now to manage their personal threat models thoughtfully.