Targeting is one of the most important elements of running effective Twitter ad campaigns. The platform provides advanced targeting capabilities to reach precise audiences and optimize Performance. This comprehensive guide explores the targeting options in Twitter Ads and best practices for Twitter Ads.
Twitter’s targeting features allow advertisers to hone in on specific demographics, interests, behaviors, and more. Strategic targeting ensures ad relevance and drives higher conversion rates.
Table of Contents
Core Targeting Approaches on Twitter
Brands can choose from a few high-level targeting frameworks based on campaign goals:
Interest-Based Targeting
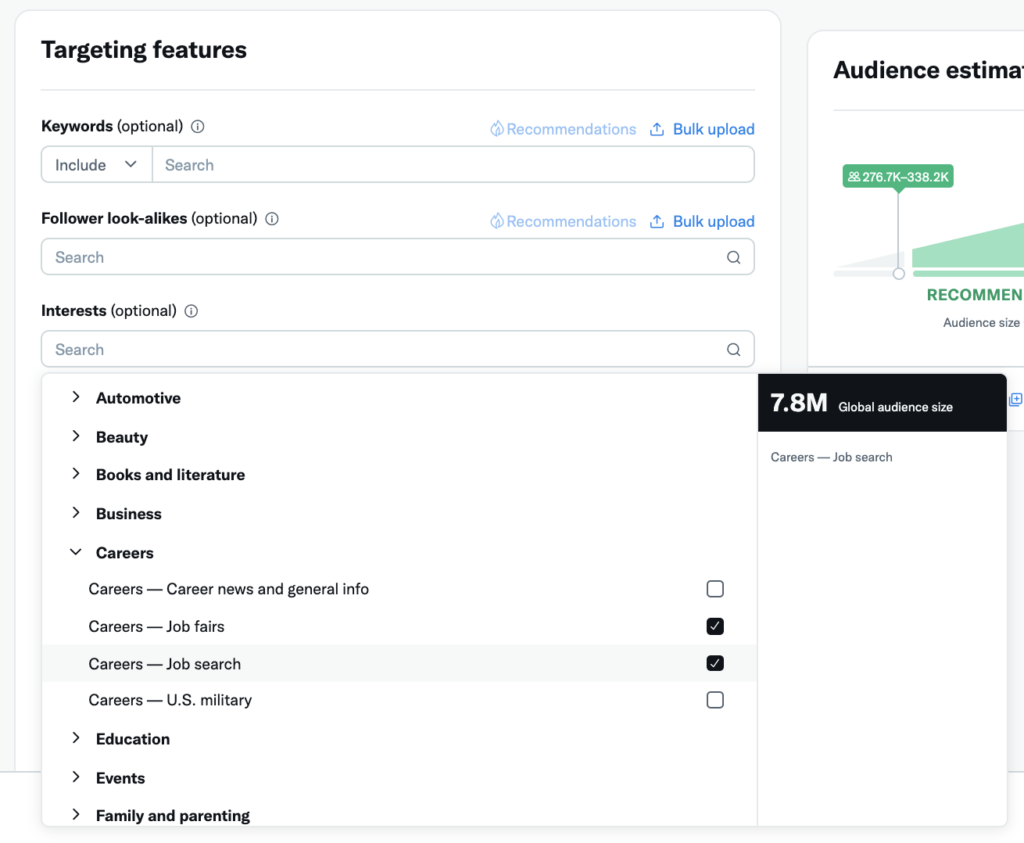
Interest targeting allows brands to serve ads to specific demographic and behavioral groups who are more likely to find their offer relevant. Some examples:
- Demographics: Age, gender, education, language, etc.
- Interests: Celebrities, food, technology, sports teams, etc.
- Behaviors: Purchase behaviors, small business owners, travelers, etc.
- Professional roles: Job titles and functions like software developers or designers.
Brands can combine dozens of interest targets to reach the ideal audience. For example, a hotel could target:
- Age 25-45
- Income $50k-$100k
- Interest in international travel
- Behavior of frequent vacationers
The more precise the interest targeting, the higher the ad relevance and engagement. Casting a wide net may get more impressions, but it sacrifices quality.
Also read: The Complete Guide to Twitter Ads Manager
Follower Look-alike Targeting
This targets new users who share similar interests with a brand’s existing Twitter followers. To create these “look-alike” audiences:
- Upload a list of current Twitter followers.
- Twitter will detect their shared interests.
- Look-alike audiences are generated based on similar users.
The main advantage is finding engaged users who resemble current brand followers to grow an audience. Sports teams or news outlets are prime examples.
Look-alike targeting works best for brands with over 1,000 followers. The larger the sample size, the better Twitter can detect interests and patterns.
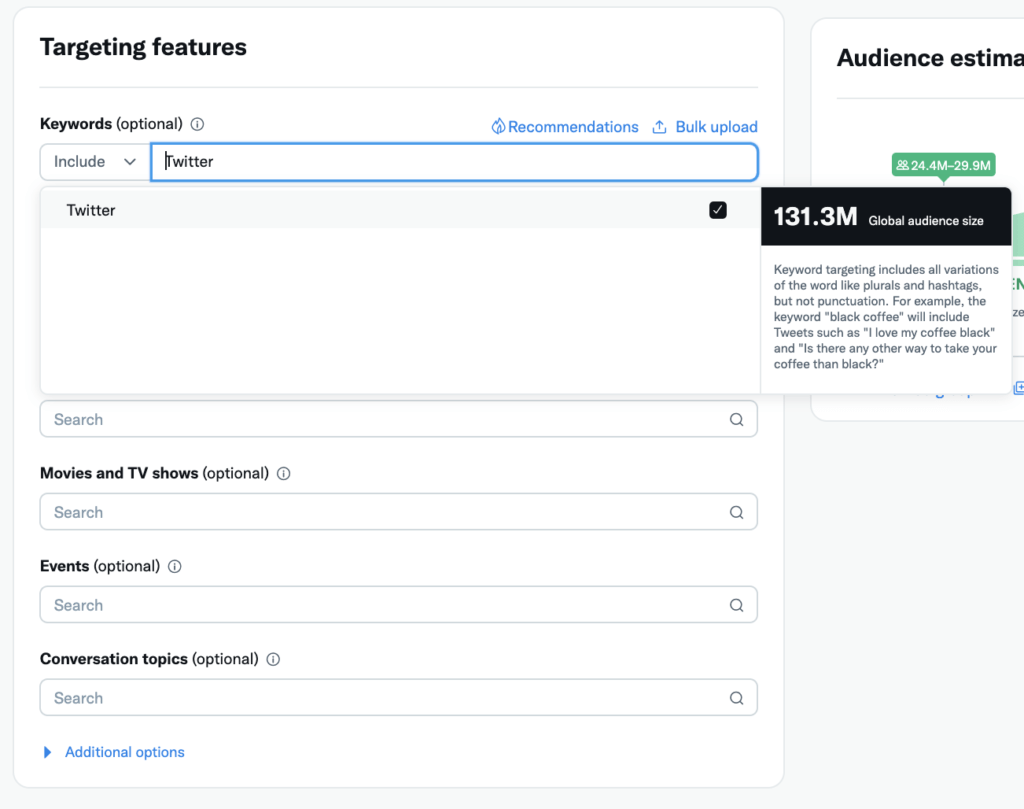
Keyword Targeting on Twitter

With keyword targeting, ads are served on Twitter when specific phrases are mentioned in Tweets. For example:
- Brand name or product keywords
- Competitor brands or products
- Industry terms and keywords
- Events, releases, or news trigger words
This approach helps brands insert their ads into relevant conversations in real-time. However, it requires closely monitoring trending topics and current events fueling word-of-mouth.
Custom Audiences on Twitter
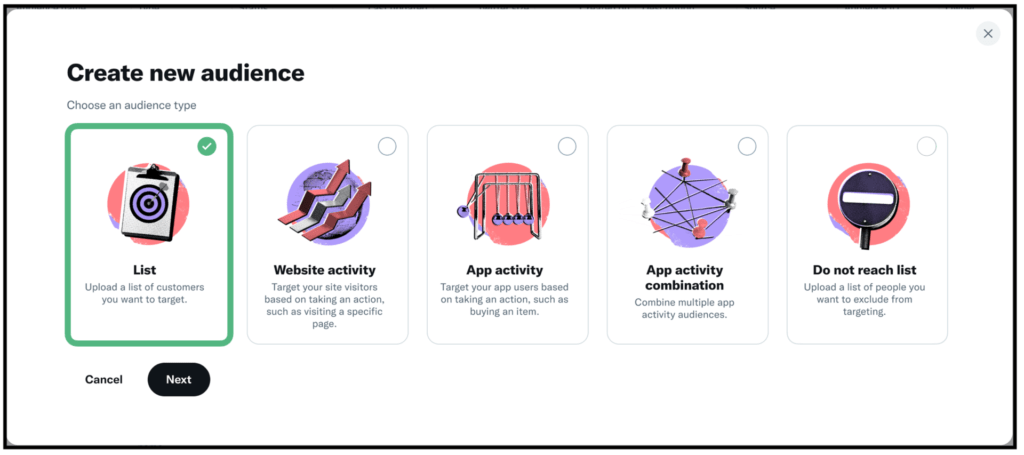
Custom Audiences allow the creation of tailored segments of users for more precise targeting:
- Website visitors: Target users who visited specific pages.
- App users: Reach people who have used a branded app.
- Email lists: Match Twitter handles to email addresses for existing subscriber lists.
- Previous ad engagers: Retarget people who engaged with past ads.
- Look-alike segments: Expand on Custom Audience with similar users.
Custom Audiences drive higher conversions by re-engaging previous site visitors or high-potential prospects. They can also inform future interest-based targeting.
Location Targeting on Twitter
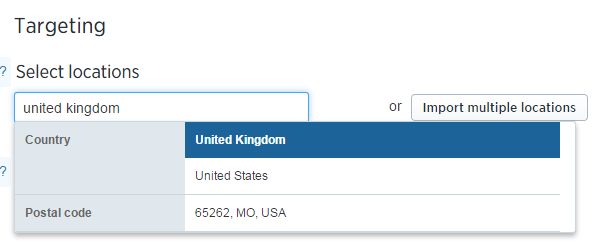
Location targeting shows ads to users in specific geographies like countries, regions, cities, or postal codes. This is ideal for:
- Brands focused on local markets or physical locations.
- Advertising events, meetups, conferences, or activations in a region.
- Area-specific campaigns and messaging.
Location can even be combined with interest targeting, for instance, targeting golf enthusiasts within 20 miles of a store location.
Combining Targeting for Precision
The most effective Twitter ad campaigns utilize multiple targeting approaches simultaneously:
- Interests layered on top of Custom Audiences
- Location added to existing interest targets
- Look-alike expansion of successful Custom Audiences
Layering approaches hone in on the highest potential customers. This increases engagement rates and conversion odds while keeping ad spend focused.
However, brands should test individual targeting methods first, then build on what delivers the strongest results. For example, master interest targeting before combining everything. Start broad, then narrow.
Optimizing Campaigns Based on Performance
The key is analyzing performance data to identify the best target segments and then optimizing spend towards those high-performing groups.
- Monitor engagement rates and conversion metrics per audience.
- Break down demographic information on website traffic.
- Continuously add new interest targets based on insights.
- Pause poor performing targets to shift budget.
- Build Custom Audiences from your top converters.
- Expand interest targeting with Look-alikes of top performers.
Consistently optimizing through data will dramatically boost Twitter Ad results over time.
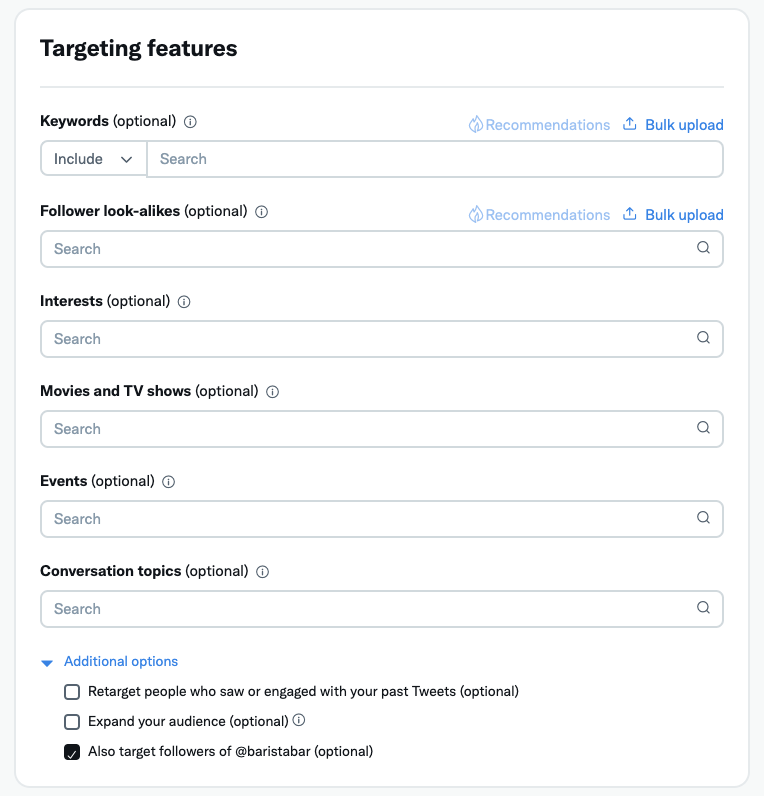
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Twitter Ads Targeting
Here is a walkthrough of actually implementing targeting in Twitter’s Ads Manager:
Step 1: Select Your Objective
- Outreach, engagement, conversions, etc. This guide recommended targeting.
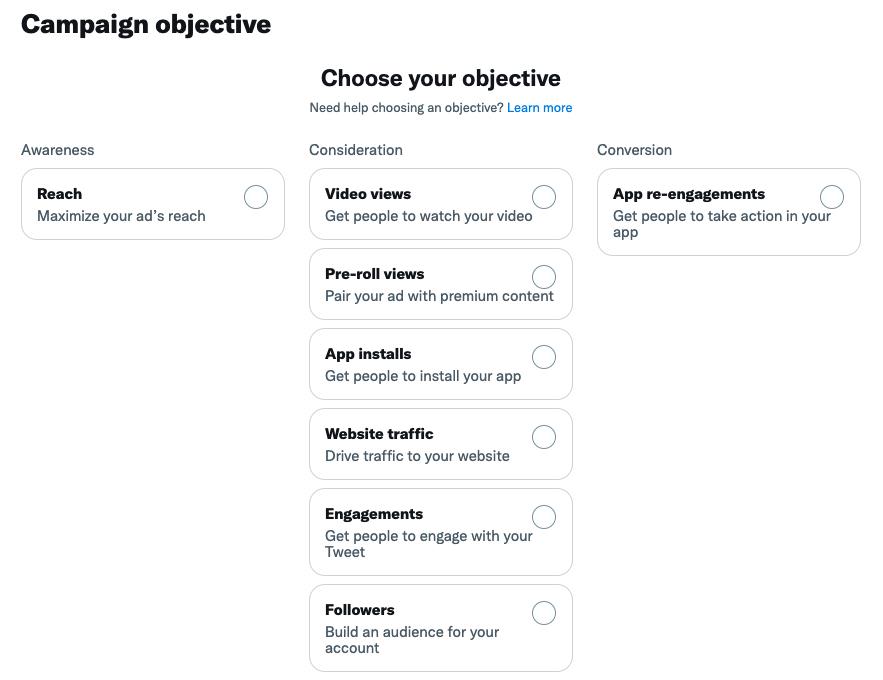
Step 2: Choose the Targeting Method
- Interest, Follower Look-alike, Custom Audience, etc.

Step 3: Configure the Target Segment
- For interests, select specific categories, keywords, etc.
- Or upload Custom Audience lists.

Step 4: Set Audience Size and Location
- Adjust age range and geography per campaign goals.

Step 5: Implement Any Exclusions
- Exclude certain interests or demographics.
Step 6: Monitor Performance
- Optimize targeting in real-time based on data.
This process enables brands to set up precise, optimized targeting in their Twitter Ads.
Twitter Targeting Case Studies
Here are some examples of brands successfully leveraging Twitter’s targeting features:
Case Study: Pet Brand Uses Interest Layering
Chewy, an online pet supplies retailer, wanted to drive visits to their dog toy section. They targeted:
- Age 25-35 (high buyer demographic)
- Interest in dogs (pet owners)
- Then layered interests in specific dog breeds.
The multiple interest layers created a tailored audience with highly relevant messaging. Chewy saw lower CPAs and 2X higher conversion rates from this audience.
Case Study: Software Company Expands with Look-alikes
HubSpot, a marketing software company, started with a Custom Audience of current users and customers. They then used Look-alike audiences to find people with similar interests to help expand their reach.
By gradually scaling through look-alikes, they extended campaigns to new audiences. HubSpot was able to grow their Twitter following 29% year-over-year.
Case Study: Gym Boosts Memberships with Keyword Targeting
A national gym chain targeted keywords related to fitness goals and “getting in shape” that spike every New Year’s. Setting bids high, their ads were seen by people tweeting New Year’s resolutions.
The timing and contextual relevance helped drive 16% more membership sign-ups in January compared to previous months.
Latest Targeting Innovations on Twitter
Here are some of the newest additions and options for targeting Twitter ads:
- Conversation targeting: Shows ads based on key phrases in Reply threads, not just main Tweets. More context.
- Interest recommendation engine: Suggest additional related interest targets based on your selections to expand reach.
- Flexible location targeting: Now allows targeting a radius around a point of interest instead of just metro regions. Better for local campaigns.
- Audience expansion: This lets you grow Custom Audiences with algorithmically suggested additional users who may fit.
- Audience exclusions: Exclude specific followings, interests, or audiences you don’t want to be targeted to refine segments.
- Category exclusives: Ad placements are only shown to #FirstView viewers who haven’t recently seen another ad in the category. Less waste.
Twitter constantly enhances targeting to provide more precision, flexibility, and scale. Staying on top of new options will allow brands to create better-tailored audiences.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Targeting on Twitter
Some emerging targeting capabilities we may see Twitter roll out include:
- Cross-platform Custom Audiences: Target users based on behaviors across multiple sites and apps, not just Twitter.
- Email address targeting: Serve ads to people based on matching email addresses to Twitter accounts.
- Offline purchase data: Incorporate CRM data on real-world purchase behaviors for online-to-offline targeting.
- Predictive audiences: Target look-alike segments based on machine learning algorithms and how audiences may respond.
- Contextual behavioral targeting: Target ads based on real-time contexts like devices, weather, and locations.
As ad targeting continues to become more automated and personalized via AI and machine learning, Twitter Ads will be able to reach customers with hyper-specific messaging in the moments they are most likely to convert.
Conclusion
Strategic audience targeting is imperative to running successful Twitter ad campaigns. Brands should leverage interest, keyword, location, Custom Audience, and look-alike targeting to reach the accounts most likely to engage.
Continuously analyzing performance data to optimize targets and increase relevancy over time can dramatically improve results. As Twitter expands its targeting capabilities, marketers have more power than ever to connect with true potential customers.
With compelling creative and solid measurement, advanced targeting is the key to high conversion rates and maximum ROAS on ad spend. For any brand looking to cut through the noise on Twitter, targeted advertising must serve as the foundation.