LinkedIn advertising can be a powerful way to reach your target B2B audience. But to get the most out of your ad spend, you need to optimize for lower Cost Per Click (CPC) and higher Click Through Rate (CTR). This results in a lower Cost Per Mille (CPM), meaning you pay less per 1,000 impressions.
But before you can reap the benefits of LinkedIn advertising, you need to understand the key pricing model: CPM, or cost per mille.
CPM determines how much you pay to have your ads seen by 1000 viewers. Mastering LinkedIn CPM is crucial for running profitable ad campaigns.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know to improve LinkedIn CPM and increase campaign performance.
Table of Contents
What is LinkedIn CPM?
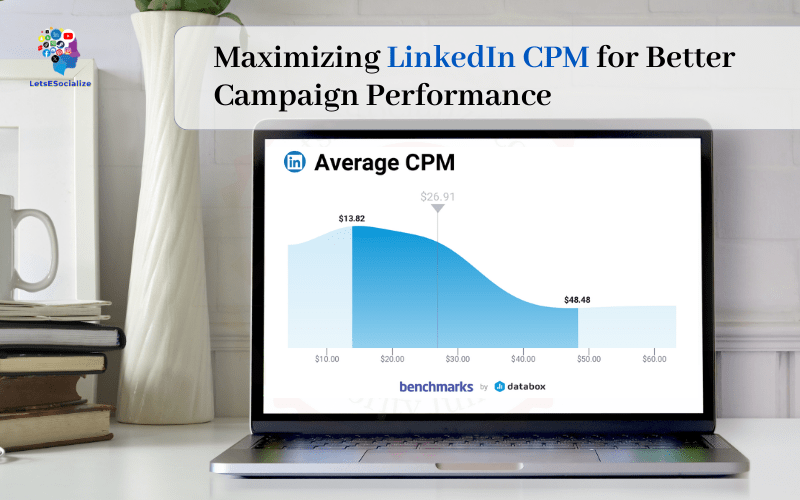
CPM stands for “cost per mille” which means the cost per thousand impressions.
An impression refers to one instance of an ad being displayed. It doesn’t matter if the ad is clicked or interacted with at all. Each display counts as one impression.
LinkedIn CPM determines how much you pay each time your ads are shown to 1000 viewers.
CPM is calculated as:
CPM = Advertising Cost / Impressions x 1000For example, if you spent $100 to receive 50,000 impressions, your CPM would be:
$100 / 50,000 x 1000 = $2 CPMLower CPM is better for advertisers. It means you’re paying less to get your ads seen. Factors like targeting, relevance, creativity, and competition all impact CPM.
CPM is the core pricing model behind LinkedIn ads:
- LinkedIn Sponsored Content is purchased on a CPM basis
- LinkedIn Text Ads are purchased on a CPM basis
- Dynamic Ads and Audience Network ads run as CPM campaigns
Understanding how LinkedIn CPM works is key to running profitable LinkedIn ad campaigns.
Also read: What is LinkedIn Sales Navigator? The Complete Guide
What is CPM in Advertising?
CPM stands for Cost Per Mille or Cost Per Thousand impressions. It is a common pricing model used in advertising, especially for digital media platforms.
In CPM advertising, advertisers are charged for every 1,000 impressions of their ad. Impressions refer to the number of times an ad is displayed. So if an ad receives 5,000 impressions, the cost to the advertiser would be 5 times the CPM rate.
Some key things to know about CPM advertising:
- Used heavily in display, social media, and native advertising to reach broad audiences
- Allows advertisers to control costs by setting daily budget caps
- A cost-efficient way to increase brand awareness and visibility
- Price set based on audience demographic, ad placement, platform, etc.
- Performance metrics include click-through rate (CTR) and conversion rate
- Advertisers only pay when the ad is displayed, ideal for brand awareness goals
So in summary, CPM advertising is a pricing model where advertisers pay for ad impressions rather than clicks or actions. It provides predictable reach based on budget.
Also read: How to Cancel LinkedIn Learning
How LinkedIn CPM Rates Work
LinkedIn charges CPM rates based on a second price auction. Here’s how it works:
- You set a maximum CPM bid when creating your LinkedIn ad campaign. This is the most you’re willing to pay.
- When your ad is eligible to show, LinkedIn runs an auction to determine which ad to display.
- All eligible ads submit their maximum CPM bids. The highest bidder wins the auction.
- The winner pays the second highest bid price instead of their max. This is called the second price auction.
For example:
- You bid a max CPM of $10
- Advertiser B bids a max CPM of $8
- Advertiser C bids a max CPM of $6
You win the auction with the highest $10 bid. But you only pay the second-highest bid of $8.
This method incentivizes advertisers to bid their true value, while paying a fair market-rate CPM.
LinkedIn recommends bidding high enough to win auctions and meet campaign goals. Bidding too low risks losing auctions and missing out on impressions.
Also read: Upskilling with AI: free LinkedIn courses to master Generative AI
What is a Good LinkedIn CPM?
LinkedIn advertising is a highly effective way to reach professional audiences relevant to your business. But with a limited ad budget, it’s important to optimize your LinkedIn ad spend and aim for a good Cost Per Mille (CPM) rate. So what CPM should you target to get the best bang for your buck on LinkedIn?
As a benchmark, LinkedIn itself recommends aiming for an average CPM between $8-12. At this rate, you can achieve good reach and frequency without overspending. Of course, your ideal CPM depends on factors like your industry, target audience, campaign objectives and more.
Here are some tips on optimizing for a good LinkedIn CPM:
Narrow Your Targeting
The more precise you can be with your ad targeting, the lower your CPM is likely to be. Target by job title, company, interests, seniority level, etc. However, don’t compromise too much on relevance. Finding the right balance leads to ideal CPMs.
Test Different Bid Strategies
Start with LinkedIn’s suggested bid range, then experiment with slightly higher and lower CPM bids to find a sweet spot. Lower CPM bids get you more impressions for your budget but may compromise reach.
Benchmark Against Your Industry
Average CPM varies significantly by industry. For example, legal or accounting CPM may be $20+ while consumer services CPM could be under $10. See what’s working for competitors in your space.
Analyze Performance Metrics
Along with CPM, look at click-through, conversion and cost per conversion rates. A very low CPM might not generate enough results. Find the balance between volume and quality.
Refine Over Time
As LinkedIn gathers data on your campaigns, it can better optimize delivery. CPM may improve as relevance increases. Continually review and tweak your targeting, creative and bids.
Aiming for a CPM around $10-15 is a good starting point for many LinkedIn advertisers. But with testing and optimization, you can often achieve strong results at even lower CPM levels over time. Measure across key metrics and improve campaign efficiency for your best LinkedIn advertising ROI.
Also read: LinkedIn Reaches 1 Billion Members, Unveils AI Job Search Tools
Factors That Impact Your LinkedIn CPM
Many variables influence the CPM you’ll pay for LinkedIn ads. The main factors include:
Audience Targeting
Targeting a more niche professional audience leads to higher CPMs. Broad targeting of titles, skills, locations, and companies will reduce CPMs.
Audience Size
The smaller your target audience, the higher the CPM. Audiences under 500,000 see significant CPM bumps.
Industry
CPMs vary across industries. Finance, technology, and consulting tend to have higher rates. Education, non-profits, and government see lower CPMs.
Ad Format
Sponsored content demands the highest CPMs, followed by text ads. Message and dynamic ads are generally the cheapest.
Device Targeting
Campaigns limited to desktops have lower CPMs than mobile-only or all-device targeting.
Location
Ads targeted by country see varying CPMs based on market demand. U.S., Australia, and Western Europe tend to have higher rates.
Competition
More advertisers competing for your target audience drive up CPMs in an auction environment.
Engagement Rate
Ads with higher click and conversion rates can sustain higher CPMs profitably.
Seasonality
CPMs fluctuate across quarters and months. Q1 and Q4 tend to see CPM peaks coinciding with buying cycles.
Also read: LinkedIn AI Image Detection Research That Catches Fake Profiles
Tips to Reduce Your LinkedIn CPM
Here are 7 proven strategies to lower your LinkedIn CPM:
1. Broaden Your Audience Targeting
Avoid narrow audience segments like individual job titles or skills. Target larger professional categories like “IT Managers” or “Marketing Professionals” instead.
2. Increase Audience Size Minimums
Raise the minimum audience size for your campaigns. CPMs are lower for audiences over 500,000 vs. under 100,000 targets.
3. Test Different Audience Locations
Compare CPMs across geographies. Some regions have naturally lower demand and competition.
4. Use Less Expensive Ad Formats
Text and message ads offer more budget-friendly options compared to sponsored content.
5. Run Campaigns on Desktop
LinkedIn CPMs are typically lower for desktop vs. mobile. Optimize campaigns for desktop placements if possible.
6. Adjust Your Bidding Strategy
Try cost cap bidding to discover the floor CPM required to win auctions and meet campaign goals.
7. Improve Ad Creatives
A/B test ad copy and creatives. Higher-performing ads justify higher CPMs.
How to Calculate LinkedIn CPM
LinkedIn advertising is powered by a cost-per-mille (CPM) pricing model. This means advertisers pay for every 1,000 impressions their ads receive on LinkedIn. But how exactly do you calculate what your LinkedIn CPM is? Here are the key steps:
- Determine Impressions
First, find the total number of impressions your LinkedIn ad campaign received for a given time period. You can find this in your LinkedIn Ads Manager under the ‘Impressions’ column.
- Determine Cost
Next, note down the total amount you spent on the LinkedIn ad campaign for the same time period. Make sure to exclude any fees and focus just on the media ad spend.
- Calculate CPM
To determine CPM, simply divide the total cost by overall impressions, then multiply by 1,000.
For example, if your campaign had 300,000 impressions over one month, at a spend of $3,000, the calculation would be:
$3,000 / 300,000 x 1,000 = $10 CPM
So your LinkedIn CPM for this campaign is $10.
- Compare to Benchmarks
See how your CPM stacks up against LinkedIn’s recommended $8-$12 CPM range and benchmarks for your target industry. This can help you optimize future campaign performance.
- Segment Data
You can drill down further by calculating CPM for different campaigns, ad sets, creatives, audiences etc. See what messaging and targeting is the most cost-efficient.
Regularly monitoring your LinkedIn CPM is key to ensuring you are getting the best value from your ad spend. Use it to make data-driven optimizations and boost results over time.
How to Calculate LinkedIn CPC and CTR
When running LinkedIn ads, it’s important to track key metrics like CPC and CTR to gauge performance. Here’s how to calculate these metrics:
LinkedIn CPC
CPC stands for cost-per-click, meaning how much you pay each time someone clicks your LinkedIn ad. To determine CPC:
- Find clicks: The number of clicks your ad received
- Find cost: Your total ad spend
- Calculate CPC: Divide cost by clicks
For example, if your ad got 300 clicks at a cost of $150, your CPC is $0.50 ($150/300 clicks).
LinkedIn CTR
CTR or click-through rate tells you how often people click your ad vs. the times it’s shown. To get CTR:
- Find clicks (same as above)
- Find impressions: The number of times your ad is displayed
- Calculate CTR: Divide clicks by impressions
So if your ad got 300 clicks with 30,000 impressions, your CTR is 1% (300/30,000).
Benchmarks
As benchmarks, LinkedIn reports average CPCs of $1-2 and CTRs of 0.5-0.8% across industries. Compare your metrics to see if you’re above or below.
Optimization
Use CPC and CTR data to guide optimization. For example, if CTR is low, work on creating better/more engaging ad creatives. Or bid higher per click to get more visibility.
Analyzing CPC and CTR is crucial for maximizing LinkedIn ad results and making data-driven decisions. Tracking these key metrics ensures you get the most value from your ad spending.
Also read: How to Change LinkedIn Password
How to Calculate LinkedIn Ad ROI
Return on investment (ROI) is a key metric that helps you determine the overall profitability of your LinkedIn ad campaigns. Here is how to calculate LinkedIn ad ROI with an example:
Identify Campaign Results
First, pull the tangible results and metrics from your LinkedIn campaign for a set time period. For example:
- Impressions: 50,000
- Clicks: 500
- Leads generated: 20
- Total revenue from leads: $2,000
Determine Ad Spend
Next, note down the total ad dollars you spent to generate those results during the same period. For example, $500.
Calculate ROI
Use this formula:
ROI = (Revenue – Ad Spend) / Ad Spend
Plug in the numbers:
ROI = ($2,000 – $500) / $500 = 300%
So for every $1 spent, this LinkedIn ad generated $3 in revenue, giving an impressive 300% ROI.
Optimize Campaigns
Compare ROI across campaigns and ad variations. Duplicate what’s working and eliminate what’s not giving your desired ROI.
Tracking LinkedIn ad ROI gives clear visibility into profitability. Aim for at least a 2-3x return on your LinkedIn investment as a good benchmark.
Current LinkedIn Advertising Rate Limits
LinkedIn enforces daily ad spend limits to ensure delivery quality and prevent issues like account suspension. Rate limits apply to both self-serve and managed accounts.
Here are the current LinkedIn ad daily spend limits as of October 2023:
| Account Type | Daily Limit |
|---|---|
| Personal Account | $25 |
| Business Account | $15,000 |
| Team Accounts | $100,000 |
Keep these limits in mind when budgeting. If you need to increase limits, you can request higher spending permissions from LinkedIn.
For managed accounts, your total limit depends on assigned capacity via your LinkedIn reps.
Note limits reset at midnight UTC daily. You cannot pre-spend your daily allocation in advance.
How to Create a LinkedIn Ad Campaign
Ready to get started with your own LinkedIn ad campaigns? Here is a step-by-step guide to creating effective LinkedIn ads optimized for your target CPM.
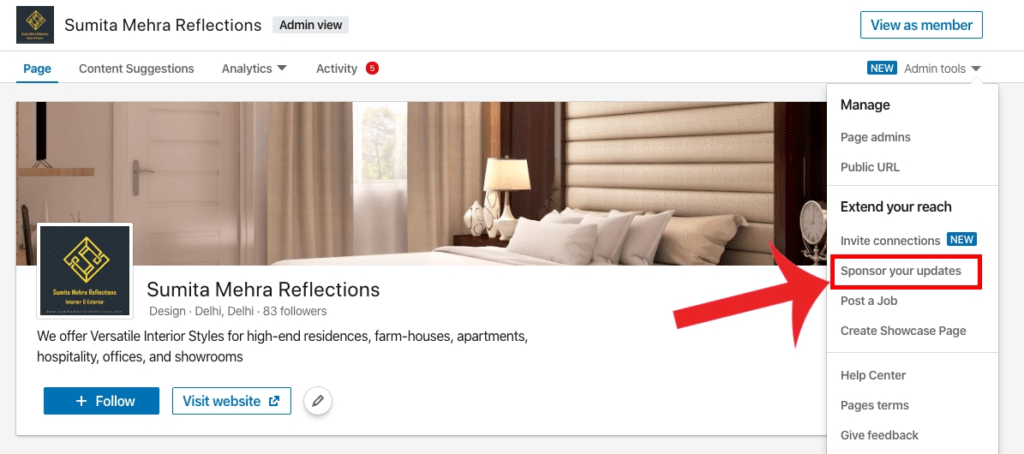
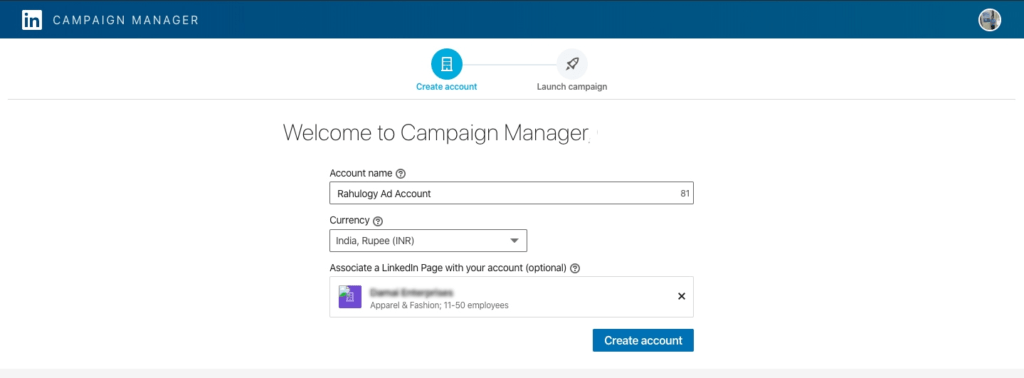
Step 1: Create an Ad account
- To create an ad account, open your company page & navigate to the “Admin Tools” menu on the top right corner below “View as member” button.
- Now choose “Sponsor your updates” option from the dropdown menu.
- Click campaign manager page with an account opening
Step 2: Set Campaign Objectives
First, clarify your campaign goals and desired actions. Common objectives include:
- Generate leads
- Drive traffic to your site
- Increase brand awareness
- Promote content
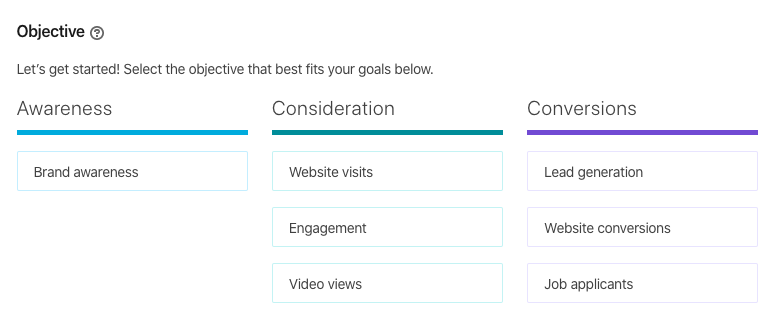
Matching objectives to the right success metrics is key (e.g. leads for lead gen).
Step 3: Define Your Target Audience
Research your ideal customer profile. Who are you trying to reach? Some factors to consider:
- Job titles and seniority
- Industries
- Skills
- Company attributes like size and revenue
- Location
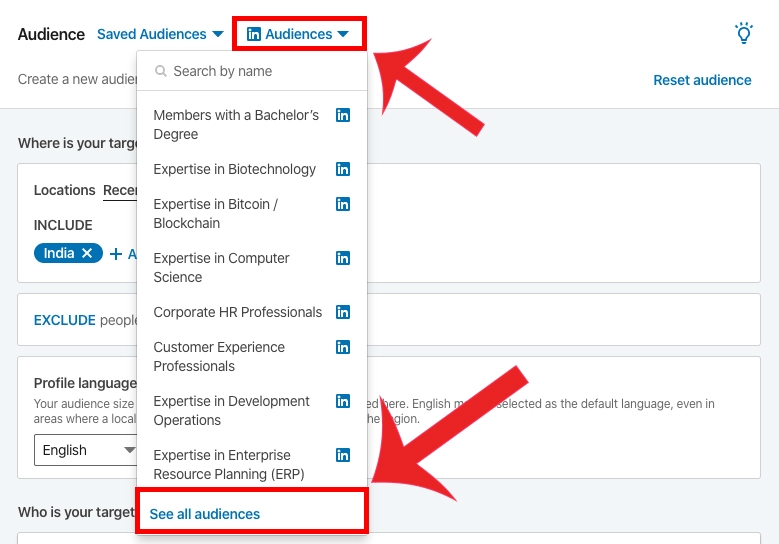
The more niche your targeting, the higher your CPM. Find the right balance of targeting to reach your goals at an acceptable CPM.
Step 4: Choose Ad Format(s)
Consider which formats are best aligned to your goals:
- Sponsored content – brand awareness and traffic
- Text ads – traffic and conversions
- Message ads – lead generation
- Dynamic ads – retargeting

Prioritize 1-2 formats to focus your budget.
Step 5: Set Your Budget
Determine how much you want to spend meeting your objectives. Budget minimums depend on the campaign objective:
- Traffic campaigns: $50/day
- Brand awareness campaigns: $500/month
- Lead generation campaigns: $300/month

Higher budgets extend your reach but aren’t a guarantee of results. Set budgets based on potential ROI.
Step 6: Set Up Bid Strategy
Pick a bidding method:
- Manual bidding – Set your max CPM bid
- Auto-bidding – Let LinkedIn algorithms bid for you
- Conversion tracking – Bid based on conversion value
- Cost cap – Pay no more than max average CPM
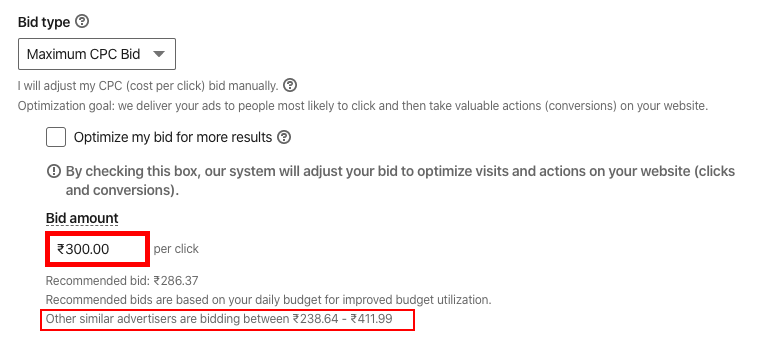
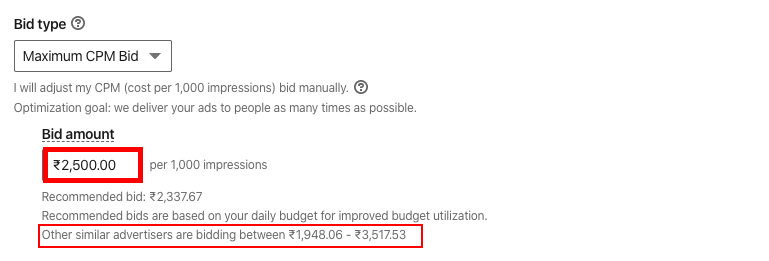
Start with manual bidding to gauge CPM. Transition to auto-bidding once you have sufficient data.
Step 7: Set up conversion tracking
Conversion tracking is an optional step in the process of setting up the campaign but it can be very helpful for you to understand how people engage on your website after clicking the ad.

Step 8: Create ads for the campaign
LinkedIn Advertising: Expert Tips and Best Practices
Ready to excel at LinkedIn advertising and slash your CPM?
Apply these proven pro tips:
Match Ad Format to Objective
Not all ad units are equal. Sponsored content builds awareness while message ads drive leads. Align your format choice to campaign goals for maximum impact.
A/B Test 2+ Ad Variations
Never place one-off bets. Develop multiple high-performing ads and rotate creatives to find the best. Testing allows you to refine CPMs downward.
Obsess Over Relevance Scores
Laser focus on relevance over vanity metrics like impressions. Higher relevance signals better targeting and lower CPMs.
Advertise on Company Pages
Company page followers are up to 4X more likely to convert versus cold audiences. Prioritize follower targeting to improve quality.
Retarget Website Visitors
Visitors who don’t convert on your site are primed for ads. Retargeting drives 2-3X higher engagement than cold outreach.
Integrate LinkedIn Insights Tag
The free tag tracks site visits from your ads. Crucial for optimizing towards real ROI rather than just CPM efficiency.
Review Reports Daily
CPMs change constantly. Stay on top of performance to adjust bids, targets, and creatives nimbly. Leverage automation to save time.
Learn Second Price Auctions
Mastering how LinkedIn auctions work lets you bid smarter. Bid high enough to win auctions while maximizing ROI.
Optimizing campaigns is an iterative process. Continual refinement over time leads to major CPM reductions and better performance.
Also read: How to Edit Your Education on LinkedIn
LinkedIn Advertising Mistakes to Avoid
On the flip side, there are several common LinkedIn advertising mistakes that inflate CPMs and hurt results. Avoid these pitfalls:
Bidding Too Low
Conservative bids mean losing auctions and opportunities. Bid competitively based on audience value.
Changing Things Too Quickly
Give changes time to take effect before making dramatic shifts. Patience pays off.
No Landing Page Strategy
Send traffic to general homepages and you’ll miss conversions. Design targeted landing pages.
Ignoring Quality Score
Low relevance causes sky high CPMs. Improve targeting and creatives to lift quality scores.
Not A/B Testing Ads
Static ads leave money on the table. Continual optimization surfaces better ads.
Focusing on CPM Alone
Don’t fixate on CPM. Look at ROI holistically, including engagement and conversions.
Chasing Impressions
Vanity metrics like reach lead advertisers astray. Prioritize driving real business outcomes.
Avoid these missteps and keep your LinkedIn ads firing on all cylinders with lower CPMs and better results over time.
Also read: How to Make LinkedIn Private: The Ultimate Guide
Tools to Analyze LinkedIn Ad Performance
To close, here are some top tools to help track and diagnose your LinkedIn CPM:
- LinkedIn Campaign Manager – LinkedIn’s dashboard for monitoring performance metrics like CPM, CPC, CTR, etc.
- LinkedIn Auction Insights – Great for analyzing the key factors driving your CPM vs. competitors.
- Google Analytics – Connect LinkedIn ads to measure engagement, conversions, and ROI holistically.
- adStage – All-in-one reporting tool for cross-channel ads. Tracks CPM, formats data, and automates reporting.
- Tableau – Advanced analytics and visualization sofware to uncover insights from LinkedIn campaign data.
- Raven Tools – Marketing analytics suite with LinkedIn campaign integration, tracking CPM and KPIs.
- Swydo – Unified reporting dashboard for LinkedIn ads and other platforms. Real-time monitoring.
- Supermetrics – Data importer to get LinkedIn data into Excel, Google Data Studio, etc. for custom analysis.
The best approach is utilizing both LinkedIn’s analytics and third-party tools for complete data coverage. Compile the insights to actively fine-tune targeting, bids, creative, and other CPM optimization tactics.
Execute a Smart LinkedIn CPM Strategy
With sky-high CPM rates on LinkedIn, implementing an intelligent cost reduction strategy is crucial. Use the targeting, bidding, ad design, analysis, and testing tips in this guide to lower CPM and maximize your ad investment.
Achieving the ideal balance of reach, engagement, conversions, and cost per impression takes work. But the long-term payoff for your LinkedIn performance makes it well worth the effort.
Now you have the actionable advice needed to monitor your key numbers, diagnostics your CPM drivers, and ultimately decrease cost per mille for your LinkedIn ad campaigns. Best of luck sparring with the LinkedIn auction algorithm! Let me know if you have any other questions.
FAQs About Reducing LinkedIn CPM
Here are answers to some commonly asked questions around optimizing LinkedIn Cost Per Mille:
-
What is a good CPM on LinkedIn?
The average global CPM is $5-7. A “good” CPM depends on your specific audience, competition, and objectives. Focus on overall ROI rather than CPM alone.
-
How much does it cost to advertise on LinkedIn?
Minimums range from $50/day for traffic campaigns up to $500/month for brand awareness. Budget based on potential ROI and start small to test performance.
-
What’s a good CPM benchmark for LinkedIn ads?
It varies widely by factors like industry and region. Global average is around $8. Anything under $10 is typically good for B2B. Target under $5 if possible.
-
Does high CTR always mean lower CPM?
Not necessarily. You can have a high CTR but also high CPC, lowering overall CPM efficiency. But generally speaking, higher engagement does correlate with lower CPM.
-
Should I use CPM or CPC bidding to reduce costs?
Try both! CPC bidding gives you more control to constrain average CPC. But CPM bidding lets you directly cap maximum CPM. See which method yields the best results.
-
What’s the minimum audience size needed for low CPM?
At least several thousand people in your target segment is best, although it depends on your niche. Too narrow targeting risks low reach and high CPM. But don’t go broader than needed just to reduce CPM.
-
Can I lower my LinkedIn CPM?
Yes! Try adjusting targeting, expanding audience size, bidding strategies, ad variations, landing pages, and overall relevance to improve CPMs over time.
Optimizing LinkedIn CPM is a nuanced process. Continual testing and refinement leads to lower rates and bigger returns from your investment. -
Is LinkedIn advertising worth the higher CPM?
Given LinkedIn’s professional audience, it commands higher CPM but can be very effective, especially for B2B lead generation. Average CPM is not the only metric – look at overall conversion value.
-
What causes sudden increases in LinkedIn CPM?
Factors like new competitors entering auctions, targeting expansion, ad fatigue, and external events can cause CPM spikes. Try to react quickly by optimizing ads and analyzing insights.
Continue testing, tracking CPM over time, and leveraging LinkedIn’s data to answer these questions for your unique situation.